Health Insurance Premiums Continue to Soar, Straining Californians
Kirk Vartan, a general manager at A Slice of New York pizza shops in the Bay Area, knows the burden of rising health insurance costs all too well. Paying over $2,000 a month for a high-deductible plan on Covered California, Vartan values the coverage that includes his wife’s doctor, even though he finds the premiums exorbitant.
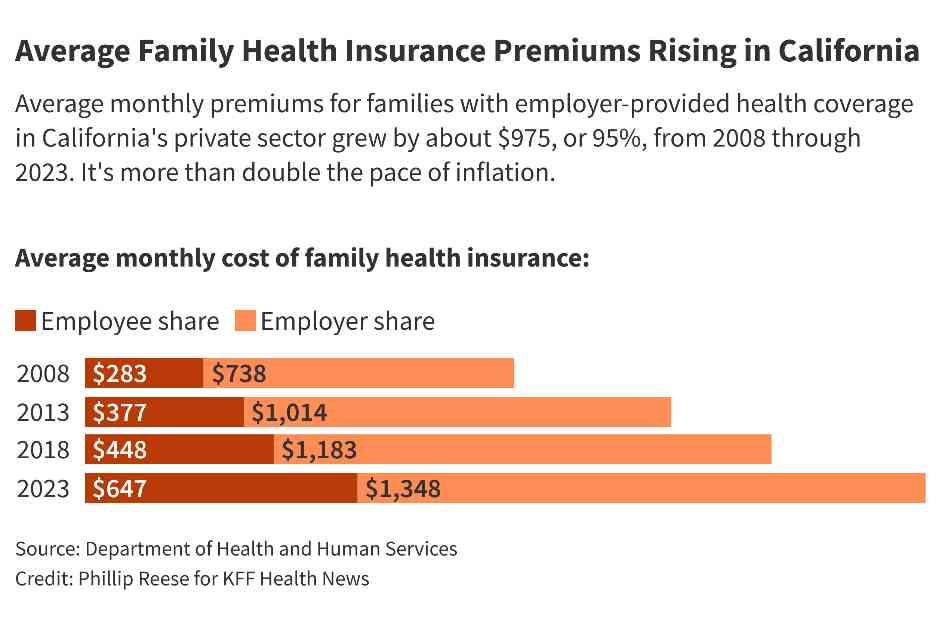
Vartan’s story is just one among millions of Californians grappling with skyrocketing health insurance premiums that are outpacing inflation rates. Families with employer-provided health coverage in California have seen their average monthly premiums nearly double over the last 15 years, according to an analysis by KFF Health News. This surge is more than twice the rate of inflation, leaving employees to bear an increasing share of the financial burden.
The situation is not unique to California. Nationwide, average premiums for families with employer-provided health coverage have grown at a similar pace. The trend has persisted into 2024, with premiums continuing to rise, posing a significant financial challenge for many Americans.
Impact on Small Businesses and Workers
Small-business groups are particularly concerned about the implications of rising health insurance costs. Without employer-provided coverage, workers may face even greater challenges in accessing affordable health care. Enhanced federal subsidies have played a crucial role in making insurance more accessible on individual markets like Covered California, which currently insures over 1.9 million Californians.
The cost of premiums on Covered California has surged by about 25% since 2022, far exceeding the rate of inflation. However, the exchange offers vital assistance to nearly 90% of enrollees through state and federal subsidies based on income, ensuring that many families do not face insurmountable financial barriers to obtaining coverage.
Employees of public institutions, including government workers covered by CalPERS, have also felt the impact of rising premiums. With costs increasing by approximately 31% since 2022, both workers and taxpayers are bearing the brunt of escalating health insurance expenses. Negotiations between public employers and labor unions determine the distribution of premium costs, underscoring the complexity of the issue.
Factors Driving Premium Increases
Miranda Dietz, a researcher at the University of California-Berkeley Labor Center, points to rising hospital prices as a primary driver of escalating insurance premiums. Consumer costs for hospital and nursing home care have surged significantly over the past decade, surpassing the overall inflation rate. The administrative costs associated with managing the U.S. healthcare system have further contributed to the upward trajectory of premiums.
While insurance companies have maintained healthy profit margins, the rising cost of healthcare delivery has necessitated higher premiums for policyholders. Despite federal regulations mandating minimum expenditures on medical care, insurers face mounting pressures to balance profitability with affordability for consumers.
The financial strain is palpable for many families and businesses across California. The average annual cost of family health insurance in the private sector has reached approximately $24,000, with workers shouldering a growing portion of the expenses. Small businesses, in particular, are feeling the pinch as fewer employers offer health insurance, forcing employees to seek coverage through individual marketplaces.
Kirk Vartan’s experience exemplifies the challenges faced by small business owners navigating the complex landscape of health insurance. Despite efforts to secure affordable plans for his workers, Vartan’s cooperative business model lacks the bargaining power to negotiate favorable terms with insurers. The resulting dilemma underscores the broader structural issues driving premium increases.
Mark Seelig of Blue Shield of California acknowledges the impact of rising healthcare costs on premium rates, citing the company’s initiatives to address pricing challenges and enhance affordability for consumers. Yet, the underlying drivers of escalating premiums remain deeply entrenched within the broader healthcare ecosystem.
In conclusion, the mounting cost of health insurance premiums is reshaping the financial landscape for families, workers, and businesses alike. As policymakers and stakeholders grapple with strategies to contain rising costs, the urgency of addressing affordability and access to quality healthcare remains paramount. Efforts to rein in healthcare spending and promote transparency in pricing may offer a path towards a more sustainable and equitable healthcare system.